Cell Membrane – Structure and Function Diagram
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is the thin, flexible outer covering of a cell that separates the internal environment from the external surroundings. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. This unique structure allows the membrane to be selectively permeable, meaning it controls what enters and leaves the cell. Small molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide pass through easily, while larger or charged molecules require special transport proteins. This selective control helps maintain homeostasis, keeping the internal conditions of the cell stable and balanced.
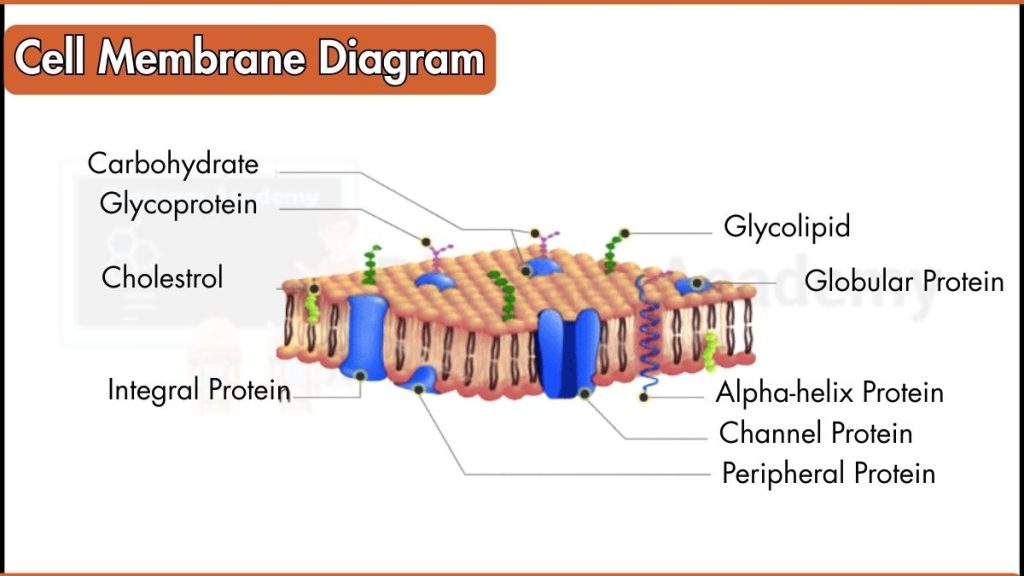
The cell membrane also plays an important role in communication and protection. Proteins on the membrane act as receptors that detect signals from the outside environment, allowing cells to respond to hormones, nutrients, and other chemical messages. Carbohydrate chains on the membrane help cells recognize each other, which is important for tissue formation and immune response. Because of its flexible and dynamic nature, the cell membrane can repair itself, transport materials, and allow the cell to interact smoothly with its surroundings. Overall, the cell membrane is essential for cell survival, movement, communication, and protection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Cell Membrane
1. What is a cell membrane?
The cell membrane is the thin, flexible outer boundary of a cell that controls what enters and leaves the cell.
2. Why is the cell membrane called selectively permeable?
It is called selectively permeable because it allows some substances to pass through while blocking others.
3. What is the main structure of the cell membrane?
It is made of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates.
4. What are the functions of the cell membrane?
Its main functions include protection, controlling transport, communication, and maintaining homeostasis.
5. What is the role of proteins in the cell membrane?
Membrane proteins help transport materials, act as receptors, and support cell recognition.
6. What is the role of cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
Cholesterol helps maintain membrane fluidity and stability.
7. How does the cell membrane maintain homeostasis?
It regulates what enters and leaves the cell, keeping the internal environment stable.
8. What molecules can easily pass through the cell membrane?
Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide pass through easily by diffusion.
9. What is the fluid mosaic model?
It describes the cell membrane as a flexible, fluid structure with proteins moving within the phospholipid bilayer like a mosaic.
10. How do large molecules enter the cell?
Large molecules enter through processes like endocytosis or by using transport proteins.
11. What is the difference between the cell membrane and cell wall?
The cell membrane is flexible and found in all cells, while the cell wall is rigid and found only in plants, fungi, and some bacteria.
12. Do all cells have a cell membrane?
Yes, every living cell—plant, animal, fungal, and bacterial—has a cell membrane.