labeled Diagram of Part of Animal cell
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus and several other membrane-bound organelles. Each organelle performs a specific function that helps the cell survive, grow, and divide.

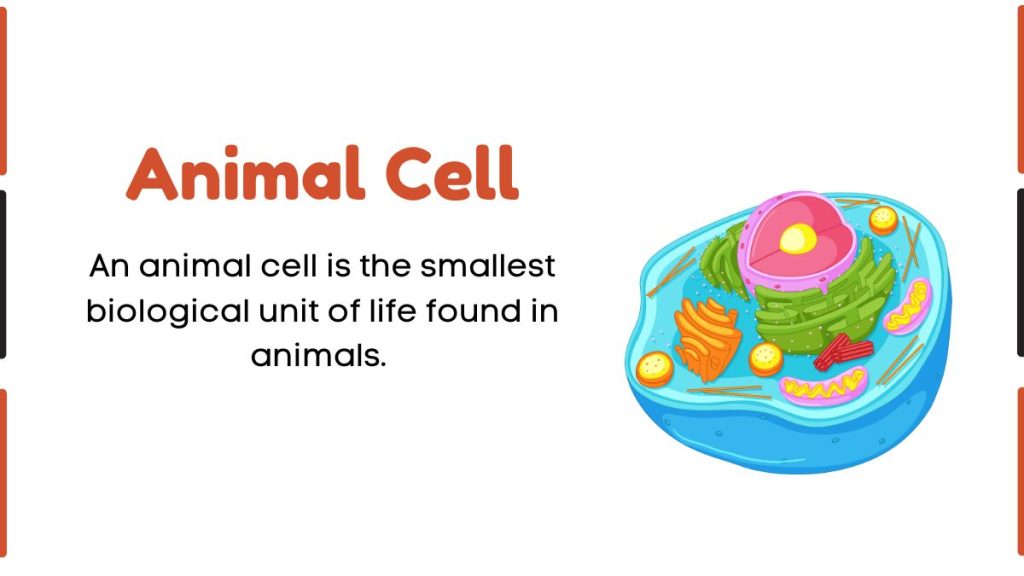

Below is a detailed explanation of the Vacuole, Nucleus, Cell Membrane, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Lysosome, using standard biological terminology.
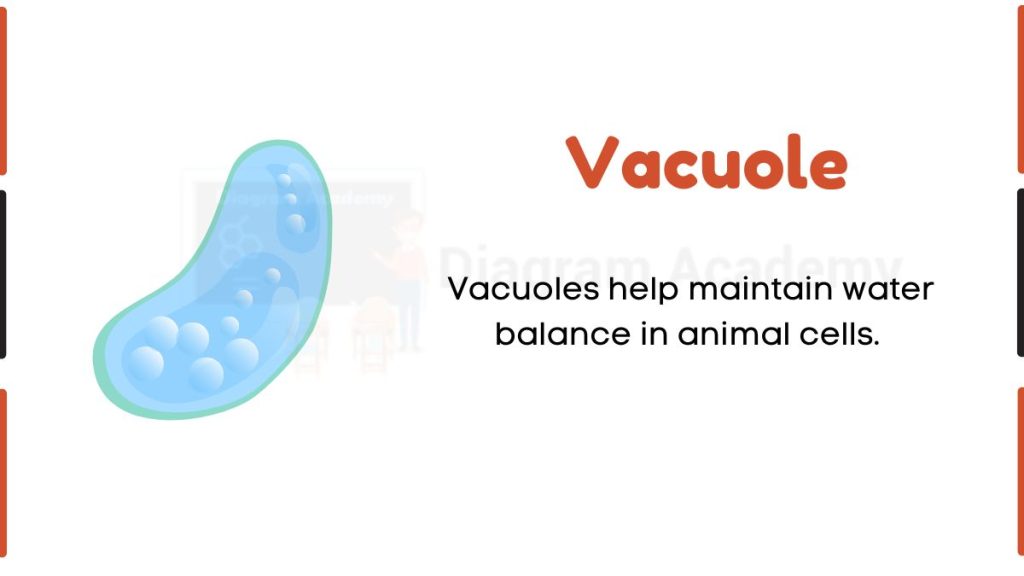
Vacuole
In animal cells, vacuoles are small, membrane-bound structures present in the cytoplasm. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not contain a large central vacuole. The vacuole helps in storage of water, ions, nutrients, and waste materials. It also plays a role in maintaining the internal balance of the cell by regulating the movement of substances. Vacuoles assist in temporary storage and help keep the cytosol free from harmful waste products.
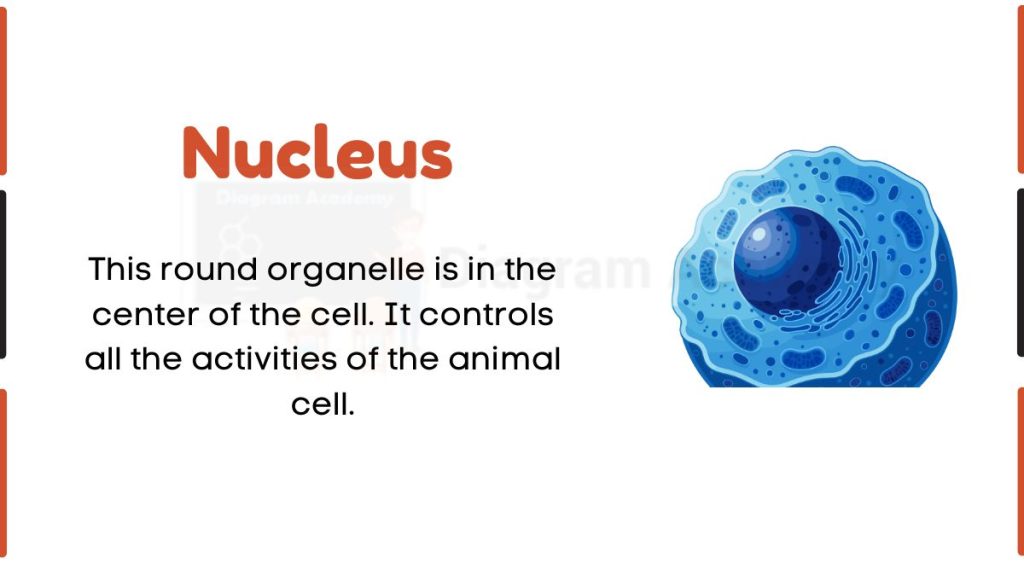
Nucleus
The nucleus is one of the most important cell organelles and is a defining feature of eukaryotic cells. It contains the genetic material DNA, which is located in the nucleolus region of the nucleus. The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell by a nuclear membrane, which controls the exchange of materials between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
The nucleus regulates the growth, metabolism, and division of cells by controlling gene expression and protein synthesis. It acts as the control center of the cell.
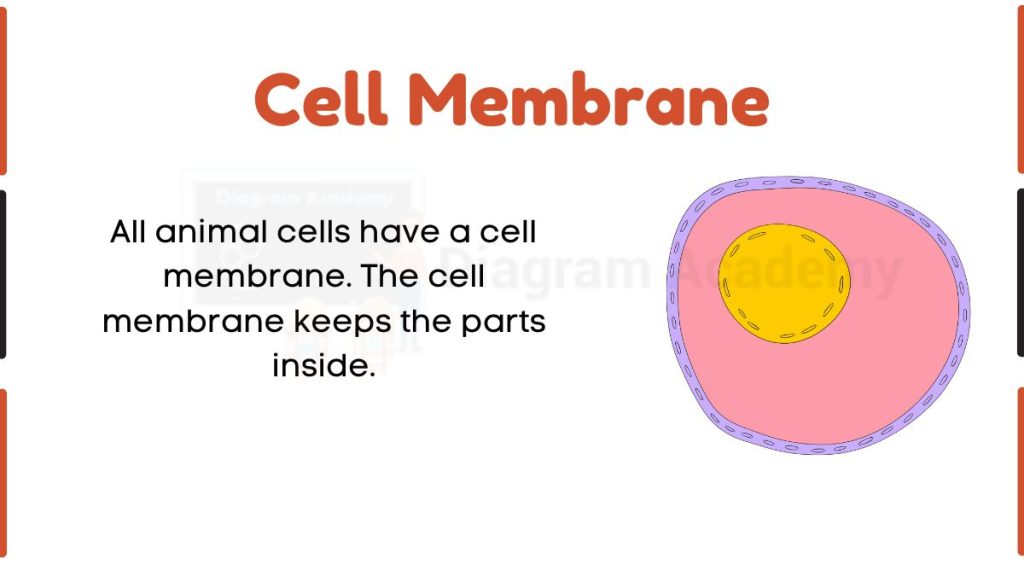
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a double-layered membrane made up of phospholipids that surrounds the entire cell. It provides protection and gives shape to the cell. The membrane is selectively permeable, meaning it allows only certain molecules to pass through while restricting others.
This property helps maintain a stable internal environment by controlling the movement of ions, nutrients, and waste materials into and out of the cell.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle involved in the modification, packaging, and transportation of proteins. It receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and packs them into vesicles.
These vesicles then transport the proteins to different parts of the cell or outside the cell. The Golgi apparatus plays a key role in the secretory pathway of the cell.

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The endoplasmic reticulum consists of a network of membranous sacs called cisternae that branch off from the nuclear membrane. It is of two types:
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) has ribosomes attached to its surface and helps in the synthesis and transport of proteins.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification processes.
Overall, the endoplasmic reticulum plays a major role in transporting proteins synthesized by ribosomes within the cell.

Mitochondria
The mitochondria is known as the “powerhouse of the cell”. It is the site of cellular respiration, a process during which energy is released in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
Mitochondria provide energy required for various cellular activities such as growth, repair, and division. Because of their role in energy production, they are essential for the survival of the cell.

Lysosome
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They help in breaking down waste materials, damaged organelles, and foreign particles present in the cell.
Lysosomes protect the cell by digesting unwanted substances and are often referred to as the “suicide bags of the cell” because they can destroy the cell if they burst and release enzymes.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are answers to common questions about Part of Animal Cell.
What are cell organelles?
Cell organelles are membrane-bound structures present within the cell that perform specific functions essential for cell survival.
Why is the nucleus called the control center of the cell?
The nucleus contains DNA and regulates growth, metabolism, and cell division, making it the control center of the cell.
What is meant by selectively permeable membrane?
A selectively permeable membrane allows only certain molecules to pass through, helping maintain the internal balance of the cell.
Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell?
Mitochondria release energy in the form of ATP during cellular respiration, supplying energy to the cell.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into vesicles for transport.
Are vacuoles large in animal cells?
No, animal cells usually contain small and temporary vacuoles, unlike plant cells which have a large central vacuole.