What Is the Orbital Diagram for Iron?
The orbital diagram for iron is a visual model that shows how electrons are arranged in the atomic orbitals of an iron atom. Unlike a simple electron configuration, the iron orbital diagram uses boxes and arrows to represent individual orbitals and electron spins. This diagram clearly explains how electrons occupy s, p, and d orbitals according to energy order.
What Atomic Information Is Required to Understand the Iron Orbital Diagram?
To interpret the orbital diagram of iron, basic atomic details are essential. Iron (Fe) has an atomic number of 26, meaning it contains 26 electrons. It is a period-4, d-block element, which explains why d orbitals play a major role in the fe orbital diagram.
How Does Electron Configuration Lead to the Iron Orbital Diagram?
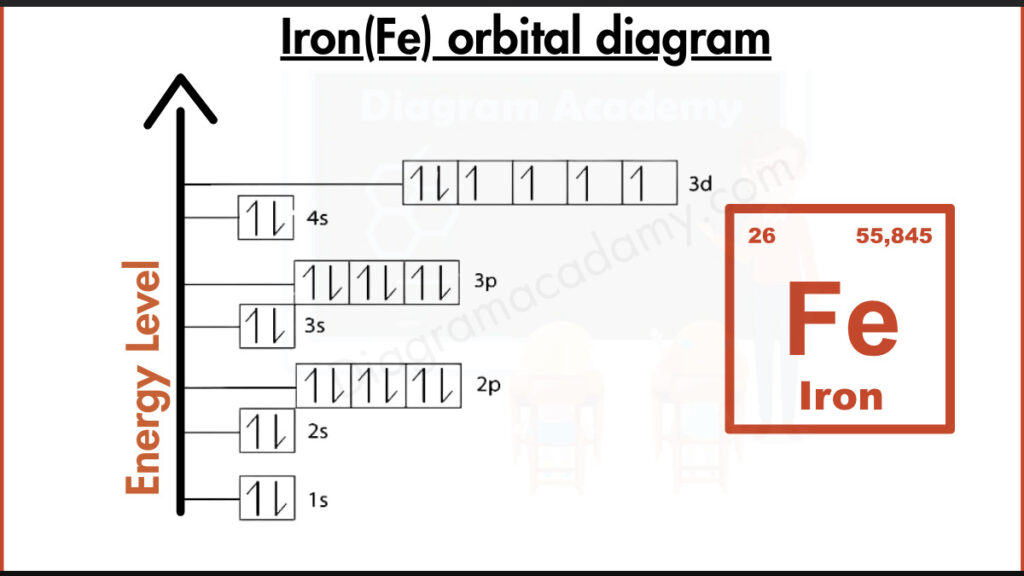
The electron configuration of iron is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁶. This configuration forms the foundation of the orbital diagram for Fe. Each orbital listed in the configuration is translated into boxes, allowing electrons to be placed visually based on spin and pairing rules.
How Is the Orbital Filling Diagram for Iron Constructed?
In the orbital filling diagram for iron, electrons fill lower-energy orbitals first following the Aufbau principle. The 4s orbital fills before the 3d orbital. Within the 3d subshell, electrons occupy separate orbitals before pairing, which is clearly shown in the orbital diagram iron using single arrows.
How Are Energy Levels Shown in the Orbital Diagram of Fe?
The orbital diagram of Fe is arranged vertically to represent increasing energy levels. Lower orbitals such as 1s and 2s appear at the bottom, while higher-energy orbitals like 3d are placed above. This structure helps learners quickly understand relative orbital energies.
What Does Orbital Notation for Iron Represent?
Orbital notation for iron visually displays electron spin using upward and downward arrows. In iron, the 3d orbitals contain unpaired electrons, which explains iron’s magnetic properties. This notation is especially useful for concept-based learning.
Why Is the Iron Orbital Diagram Important in Chemistry?
The orbital diagram for iron is important for understanding bonding behavior, oxidation states, and reactivity. It is widely used in textbooks, exams, and digital diagram resources to explain how iron behaves chemically.
Frequently Asked FAQs
Here are the answer to common question about Orbital Diagram for Iron (Fe).
Q1: What does the orbital diagram for iron show?
It shows how 26 electrons are distributed in iron’s atomic orbitals using arrows and boxes.
Q2: Why does the iron orbital diagram show 4s filling before 3d?
Because in the orbital filling diagram for iron, the 4s orbital has lower energy during initial filling.
Q3: How many unpaired electrons are in the iron orbital diagram?
The iron orbital diagram shows four unpaired electrons in the 3d orbitals.
Q4: Is orbital notation for iron the same as electron configuration?
No, orbital notation for iron shows electron spin and pairing, while configuration only lists occupancy.
Q5: Why are d orbitals important in the orbital diagram of Fe?
The d orbitals determine iron’s magnetic and chemical properties, which are clearly shown in the fe orbital diagram.