How Can the Uranium Orbital Diagram Be Defined?
The uranium orbital diagram is a visual representation showing how electrons are distributed among the atomic orbitals of a uranium atom. Unlike simple atomic models, the orbital diagram of uranium displays individual orbitals using boxes and arrows, making electron spin and orbital occupancy easy to interpret.
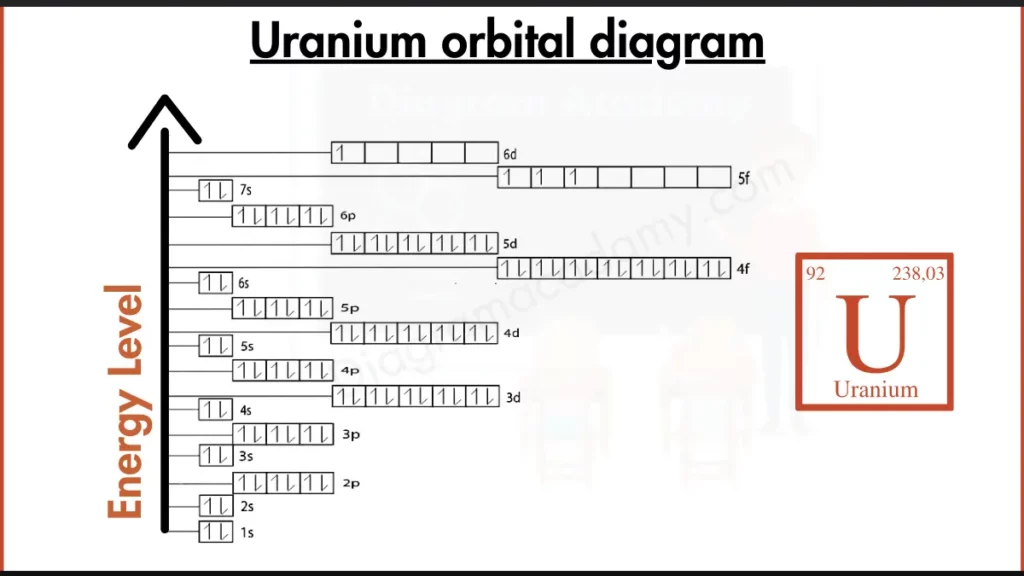
Which Atomic Facts Are Important Before Reading the Diagram of Uranium?
Uranium has the symbol U and an atomic number of 92, meaning it contains 92 electrons. It belongs to the actinide series and is located in period 7 of the periodic table. These facts help explain why f orbitals appear prominently in the diagram of uranium.
How Do Uranium Orbitals Follow Electron Configuration Rules?
The electron configuration of uranium is:
[Rn] 5f³ 6d¹ 7s²
This configuration forms the basis of the uranium electron configuration diagram, showing how electrons occupy s, d, and f orbitals according to the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle.
How Is the Orbital Diagram of Uranium Arranged Across Energy Levels?
In the orbital diagram for uranium, orbitals are arranged vertically to represent increasing energy. Lower-energy orbitals appear at the bottom, while higher-energy orbitals such as 5f and 6d appear higher. This layered structure helps viewers understand complex electron placement in heavy elements.
What Makes the Uranium Electron Configuration Diagram Unique?
The presence of partially filled 5f orbitals makes the uranium orbitals distinct from lighter elements. These f-electrons are responsible for uranium’s complex chemistry and radioactive behavior, clearly visible in a detailed orbital diagram.
How Does the Uranium Orbital Diagram Differ from a Bohr Diagram?
A uranium Bohr diagram only shows electrons in circular shells, while the orbital diagram of uranium provides precise orbital shapes, energies, and electron spins. Orbital diagrams offer a more accurate quantum-level explanation.
Why Is the Orbital Diagram for Uranium Important in Chemistry?
The orbital diagram for uranium helps explain oxidation states, bonding behavior, and nuclear properties. It is widely used in advanced chemistry education, exams, and scientific diagram references.
Frequently Asked FAQS.
Here are answers to common questions about Uranium Orbital Diagram (U).
Q1: What does the uranium orbital diagram show?
It shows how 92 electrons are arranged in uranium’s atomic orbitals using arrows and boxes.
Q2: Why are f orbitals important in the orbital diagram of uranium?
Because uranium is an actinide, its chemical behavior depends heavily on partially filled f orbitals.
Q3: Is this diagram correct for uranium?
Yes, a correct uranium orbital diagram follows the configuration [Rn] 5f³ 6d¹ 7s² and quantum rules.
Q4: How is the uranium orbital diagram different from the Bohr diagram?
The orbital diagram shows exact orbital filling and spin, while the Bohr diagram only shows shells.
Q5: Where are the highest energy electrons shown in the uranium diagram?
They appear in the 5f and 6d orbitals at the top of the diagram.