What Does the Orbital Diagram for Germanium Represent?
The orbital diagram for Ge visually shows how electrons are arranged in the atomic orbitals of a germanium atom. Instead of listing electrons numerically, the germanium orbital diagram uses boxes and arrows to display orbital occupancy and electron spin. This makes it easier to understand how electrons are distributed around the nucleus.
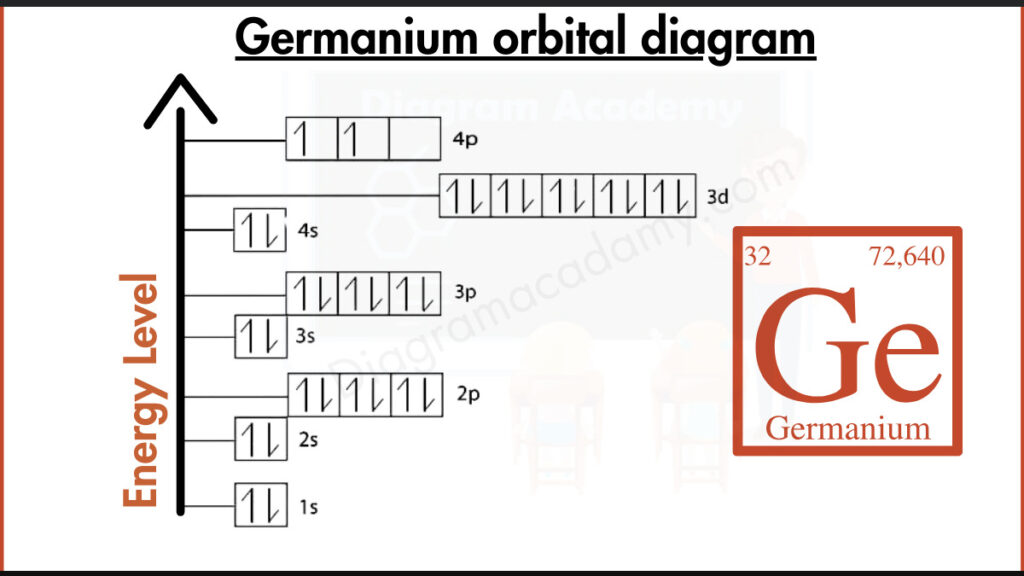
How Many Electrons Are Shown in the Ge Orbital Diagram?
Germanium has an atomic number of 32, meaning it contains 32 electrons. In the orbital diagram of germanium, these electrons are placed into s, p, and d orbitals according to increasing energy levels. Germanium belongs to the p-block and is located in period 4 of the periodic table.
How Is the Orbital Diagram of Germanium Built from Electron Configuration?
The electron configuration of germanium is:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p²
This configuration directly translates into the orbital diagram germanium, where each orbital is represented by a box and electrons are added as arrows. The filled 3d subshell and partially filled 4p subshell are key features of the orbital diagram of Ge.
How Are Valence Electrons Shown in the Orbital Diagram for Ge?
The orbital diagram for the valence electrons of Ge focuses on the outermost shell. Germanium has four valence electrons, located in the 4s² and 4p² orbitals. In the diagram, the two 4p electrons occupy separate orbitals before pairing, following Hund’s rule. This explains germanium’s bonding behavior.
What Does Germanium Orbital Notation Explain?
Germanium orbital notation visually represents electron spin and pairing. Arrows pointing in opposite directions show paired electrons, while single arrows represent unpaired electrons. This notation helps explain why germanium shows both metallic and nonmetallic properties.
Why Is the Orbital Diagram for Germanium Useful?
The orbital diagram for germanium is useful for understanding chemical bonding, conductivity, and semiconductor behavior. It is commonly used in chemistry education, exams, and diagram-based learning platforms to visually explain atomic structure.
Frequently Asked FAQs
Here are the answer to common question about Germanium Orbital Diagram (Ge).
Q1: What does the orbital diagram for Ge show?
It shows how 32 electrons are arranged in germanium’s atomic orbitals using arrows and boxes.
Q2: How many valence electrons are shown in the orbital diagram of germanium?
The orbital diagram shows four valence electrons in the 4s and 4p orbitals.
Q3: Why are the 4p electrons unpaired in the germanium orbital diagram?
Because electrons fill separate p orbitals first according to Hund’s rule.
Q4: Is germanium orbital notation different from electron configuration?
Yes, orbital notation visually shows spin and pairing, while configuration lists electrons numerically.
Q5: Why is the orbital diagram for germanium important?
It helps explain germanium’s bonding behavior and its role as a semiconductor.