Diagram of Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
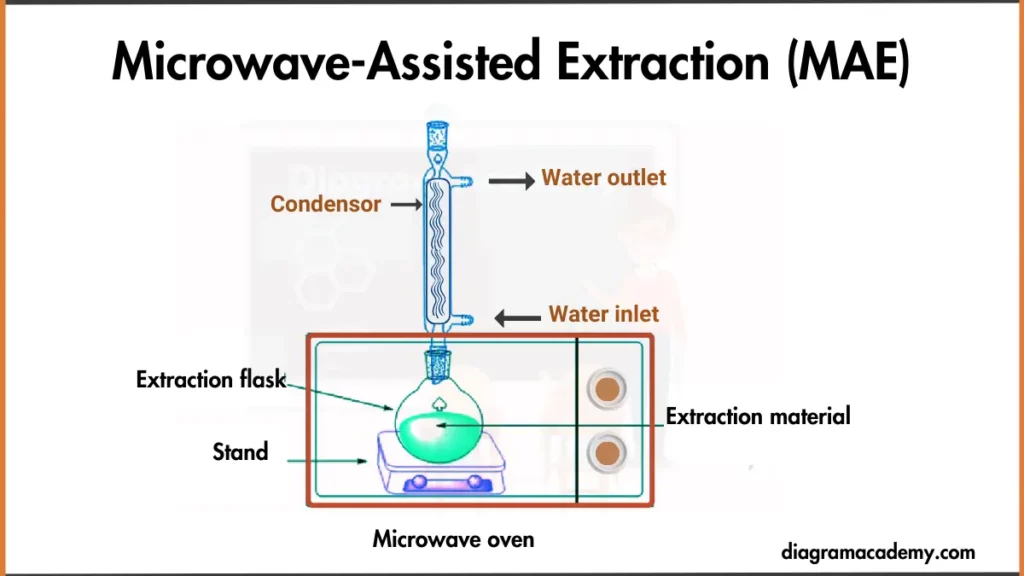
Working principle of Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE) is a method of extracting compounds from a sample using microwave energy to heat a solvent mixture. The rapid heating and pressure buildup enhance the extraction efficiency by breaking down cell walls and facilitating the release of target compounds into the solvent.
Here are some general Working principle of Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE):
- Microwave Heating: First, we place sample and solvent in a sealed container. Now we turn on microwave to zap solvent molecules, causing them to vibrate and heat up rapidly.
- Pressure Build-Up: As mixture heats, pressure increases inside sealed container. Increased pressure enhances solvent’s ability to extract target compounds from the sample.
- Cell Wall Breakdown: Heating from microwaves weakens cell walls of sample. This facilitates the release of target compounds into the solvent for extraction.