Diagram of Circulatory system of human
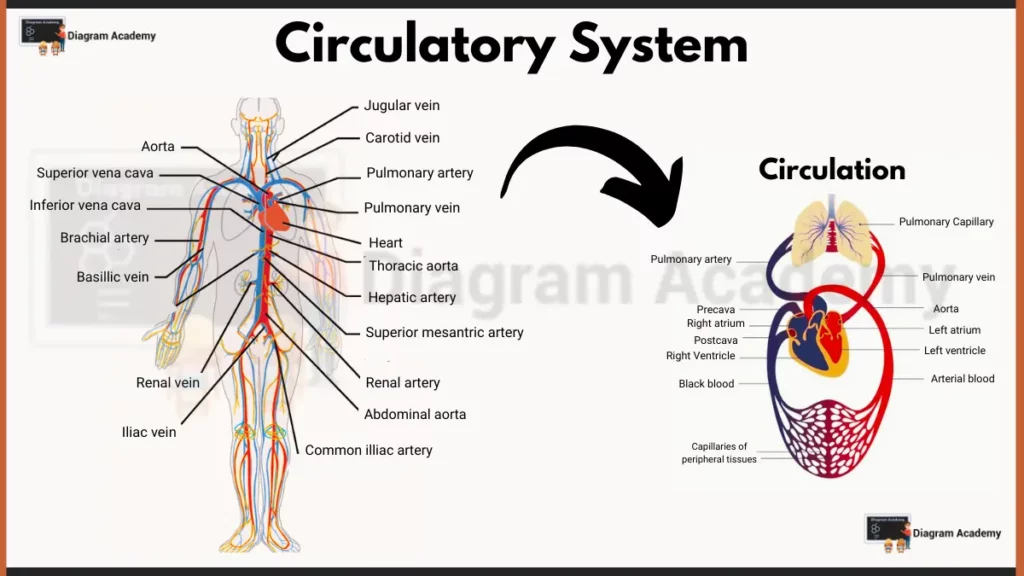
Above diagram represents the Human Circulatory System, which is responsible for transporting blood throughout the body.
Here are the main parts of human circulatory system and their functions:
1. Blood Vessels
- Arteries: carry arterial blood (oxygen-rich) away from the heart.
- Aorta: the largest artery, branching out to other arteries.
- Brachial artery: supplies blood to the arm.
- Thoracic aorta: section of the aorta in the chest cavity.
- Abdominal aorta: section of the aorta in the abdominal cavity.
- Hepatic artery: supplies blood to the liver.
- Superior mesenteric artery: supplies blood to the small intestine and part of the large intestine.
- Renal artery: supplies blood to the kidneys.
- Common iliac artery: divides into the internal and external iliac arteries supplying blood to the lower body.
- Veins: carry deoxygenated blood (low in oxygen) back to the heart.
- Superior vena cava: drains blood from the upper body.
- Inferior vena cava: drains blood from the lower body.
- Jugular vein: drains blood from the head and neck.
- Carotid vein: drains blood from the brain.
- Subclavian vein: drains blood from the arm and shoulder.
- Hepatic vein: drains blood from the liver.
- Renal vein: drains blood from the kidneys.
- Iliac vein: drains blood from the lower body.
- Pulmonary vein: carries oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart.
- Capillaries: microscopic vessels where exchange of gases and nutrients occurs.
- Capillaries of peripheral tissues: exchange oxygen and nutrients with body cells.
- Pulmonary capillaries: exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
2. Heart Chambers
- Right atrium: receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
- Right ventricle: pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- Left atrium: receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
- Left ventricle: pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
3. Blood Flow/Circulation Pathway
1: Pulmonary circulation: blood flow between the heart and lungs for oxygenation.
Right ventricle -> Pulmonary artery -> Lungs -> Pulmonary veins -> Left atrium.
2: Systemic circulation: blood flow throughout the body delivering oxygen and nutrients.
Left ventricle -> Aorta -> Arteries -> Capillaries -> Veins -> Superior and inferior vena cava -> Right atrium.