How Can the Radium Orbital Diagram Be Defined?
The radium orbital diagram is a visual representation showing how electrons are distributed across the atomic orbitals of a radium atom. Unlike text-based configurations, the orbital diagram for radium uses boxes and arrows to clearly illustrate orbital occupancy and electron spin, making it ideal for diagram-based learning.
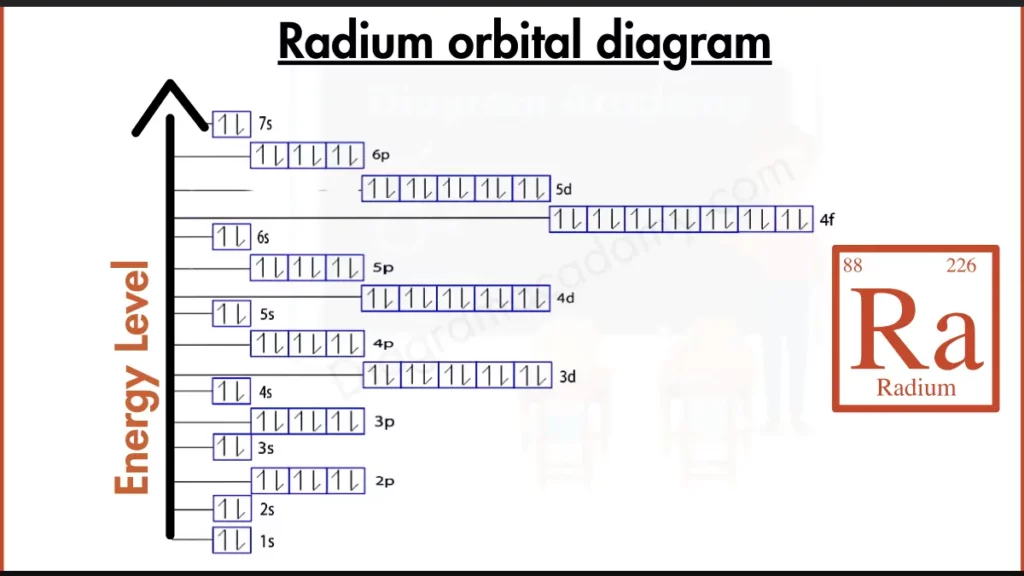
Which Atomic Facts Help Read the Orbital Diagram of Radium?
To understand the orbital diagram of radium, it is important to know that radium has the symbol Ra and an atomic number of 88, meaning it contains 88 electrons. Radium is a group 2 alkaline earth metal in period 7, which explains the presence of two electrons in its outermost shell.
How Does the Full Electron Configuration for Radium Relate to Its Orbital Diagram?
The full electron configuration for radium is based on the noble gas core [Rn] 7s². This configuration directly determines the structure of the orbital diagram of radium, where all inner orbitals are filled and the valence electrons occupy the 7s orbital.
How Are Electrons Arranged in the Orbital Diagram for Radium?
In the orbital diagram for radium, electrons fill orbitals from lower to higher energy following the Aufbau principle. Each orbital holds a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. The diagram shows paired electrons throughout, with the highest-energy electrons clearly located in the 7s orbital.
What Does Radium Orbital Notation Show in a Diagram?
Radium orbital notation uses arrows to represent electron spin within each orbital. In radium, the two valence electrons appear as a paired set in the 7s orbital. This visual notation helps explain radium’s tendency to form +2 ions.
How Is Radium Different from the Radon Orbital Diagram?
Although radium uses radon as its core, the radon orbital diagram ends with filled 6p orbitals, while the radium orbital diagram extends further to include the 7s electrons. This difference explains why radon is inert, while radium is reactive.
Why Is the Radium Orbital Diagram Useful in Chemistry?
The orbital diagram of radium helps students understand valence electrons, bonding behavior, and periodic trends. It is commonly used in chemistry diagrams, exams, and visual learning platforms to simplify complex atomic concepts.
Frequently Asked FAQs
Here are the answer to common question about Orbital Diagram of Radium (Ra).
Q1: What does the radium orbital diagram show?
It shows how 88 electrons are arranged in radium’s atomic orbitals using arrows and boxes.
Q2: How many valence electrons are shown in the orbital diagram for radium?
The orbital diagram for radium shows two valence electrons in the 7s orbital.
Q3: Why is radium more reactive than radon based on orbital diagrams?
Radium has outer 7s electrons, while radon’s outer shell is completely filled, making radon inert.
Q4: Is radium orbital notation the same as electron configuration?
No, radium orbital notation visually shows electron spin and pairing, while configuration lists electron counts.
Q5: Can the radium Lewis dot structure be predicted from the orbital diagram?
Yes, the orbital diagram shows two valence electrons, which directly determine the Lewis dot structure for radium.