Diagram of Solid-Liquid Extraction
Working Principle of Solid Liquid Extraction
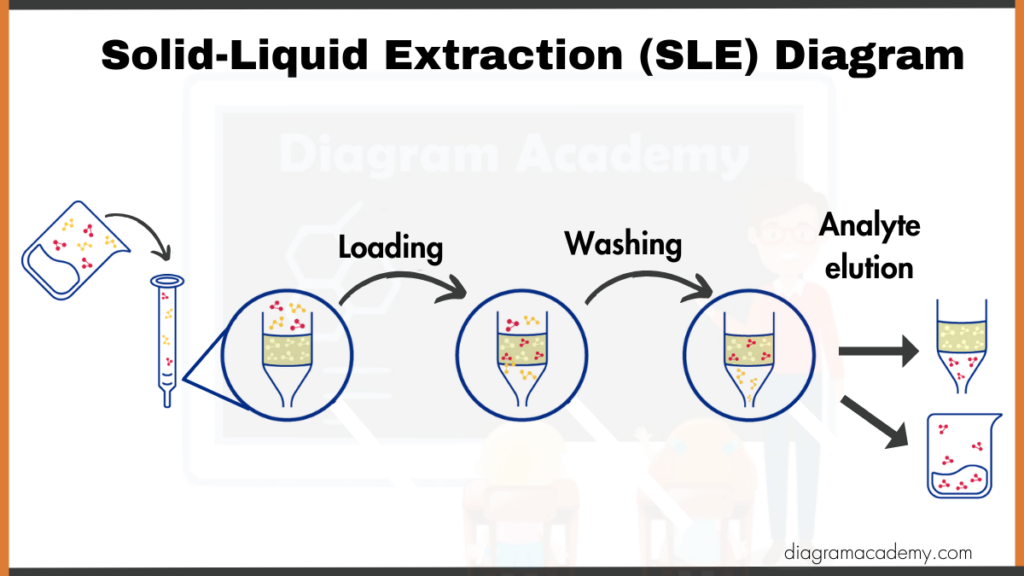
Solid-liquid extraction isolates desired components from a solid mixture by dissolving them in a suitable solvent. The soluble components are then separated from the undissolved solid material, leaving the desired extract in the liquid phase.
Here are the general working principles of solid-liquid extraction:
- Conditioning: First, we activate the stationary phase with solvent (e.g., methanol).
- Equilibration: Then we wash it with weak solvent (e.g., water) to remove conditioning solvent and prepare for sample.
- Sample loading: Then we load sample containing target compound. Target binds, unwanted components pass through.
- Washing: Now we remove weakly bound interferences with wash solvent (e.g., 10% methanol in water).
- Elution: Now desorb target compound with strong solvent (e.g., pure methanol) for collection and analysis.