Diagram of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
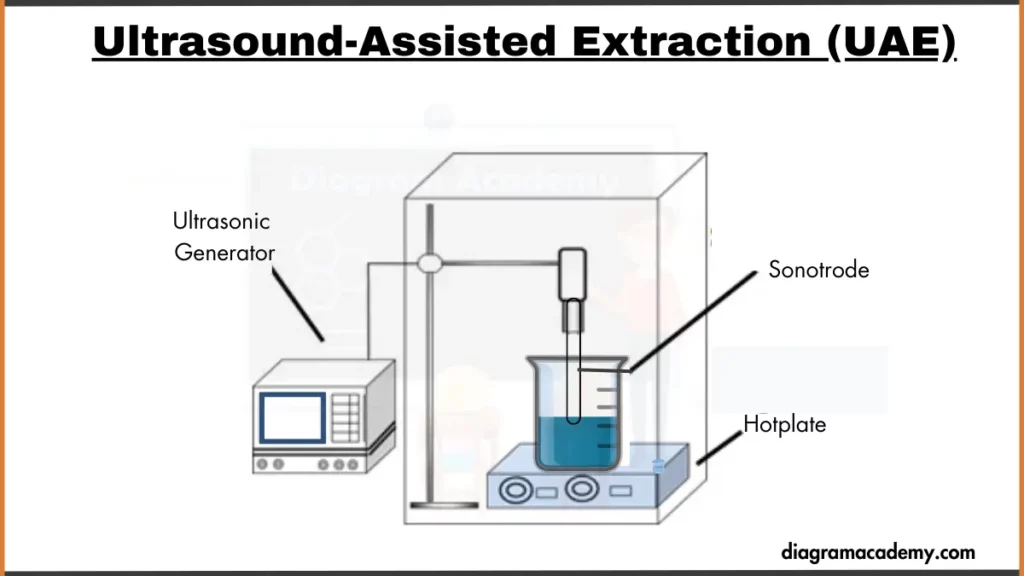
Working principles of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE) is a technique where ultrasonic waves are used to break down the cell walls of solid samples in a solvent, allowing the release of desired compounds. The high-frequency waves create tiny bubbles in the solvent, which collapse with force, aiding in the extraction process.
Here are some general Working principles of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE):
- Ultrasonic Waves Creation: First, we submerge sample and solvent in a container. Then, we Introduce ultrasonic waves at a frequency higher than audible range, causing solvent molecules to vibrate and form tiny bubbles in the mixture.
- Bubble Collapse: As ultrasonic waves propagate, the tiny bubbles experience rapid growth followed by collapse. The collapse generates intense shocks that effectively rupture the cell walls of the sample material.
- Release of Target Compounds: With the cell walls compromised, valuable compounds previously trapped within the sample are released into the solvent, facilitating extraction.